




1. Gravity separation gold extraction process
Gravity separation is one of the commonly used methods in gold ore beneficiation. Based on the difference in mineral density and particle size, mechanical force is used to achieve layered separation in the fluid medium to effectively recover coarse free gold. This method has the advantages of environmental protection and low cost. It is widely used in the treatment of placer gold mines. At the same time, it is used as an auxiliary means for the beneficiation of rock gold mines to recover coarse gold in the grinding circuit.
Common equipment includes chutes, jigs and shaking tables. Jigging gold selection is suitable for sorting coarse mineral particles with a particle size range from 50mm to 0.007mm. Chute gold selection is suitable for low-grade placer gold mines and for processing fine-grained materials with low mud content. The material particle size range is 0.6~0.03mm and the recovery rate can reach 60%-90%. It has the characteristics of simple structure, large processing capacity and low cost. The shaking table gold selection is suitable for materials with finer particle sizes, ranging from 3 to 0.019 mm. The gold selection process is stable and reliable, with a high rich ore ratio and easy management. In vein gold mines, gravity separation is often used in combination with other processes to improve the overall beneficiation efficiency and gold recovery rate.
2. Flotation gold extraction process
Flotation is widely used in gold ore beneficiation, especially for treating gold-bearing ores containing highly floatable sulfide minerals. Because gold is hydrophobic and has good floatability, yellow medicine and black medicine are used as collectors, combined with inhibitors such as lime, cyanide and sodium sulfide, to effectively enrich gold and sulfide minerals into concentrates. The flotation method can not only efficiently recover gold, but also realize the comprehensive utilization of multiple metals, such as by enriching gold into copper and lead concentrates for further extraction. For gold ores with uniform and coarse particle size, a grinding and flotation process is usually used. For difficult-to-treat ores, flotation is often used as part of a combined process to effectively improve the gold recovery rate. However, since gold is usually enriched in sulfide concentrates, flotation usually needs to be used in conjunction with other processes, such as cyanide leaching, roasting or high acid washing, to achieve effective gold recovery.
3. Cyanide gold extraction process
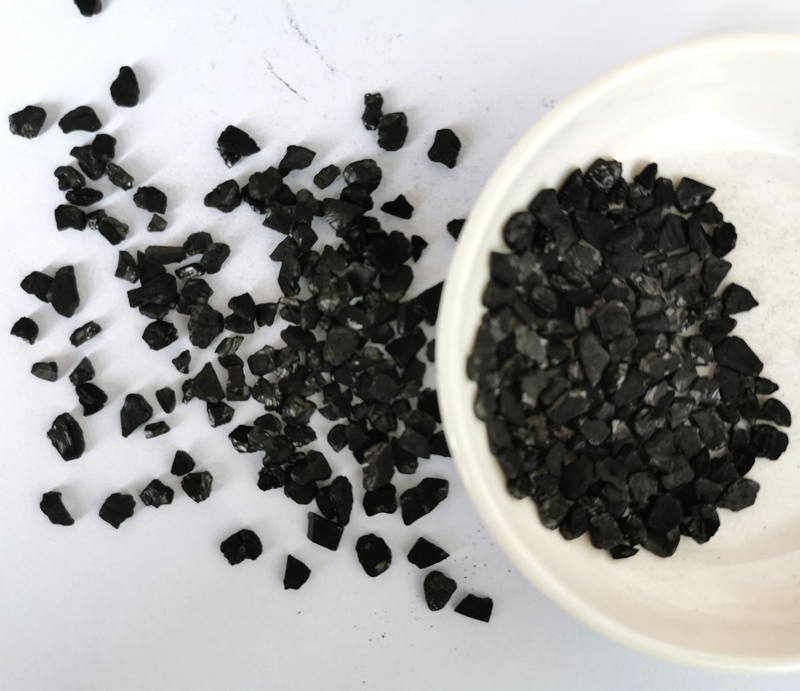
As the main process for efficient gold recovery, cyanide is particularly suitable for treating gold-containing oxidized ores with high ore mud content. Cyanide leaching is performed on the crushed and ground ore, and cyanide ions react with gold to form a complex that dissolves in the solution, and then is adsorbed on activated carbon, electrolyzed or replaced with zinc powder, and then smelted to extract gold.
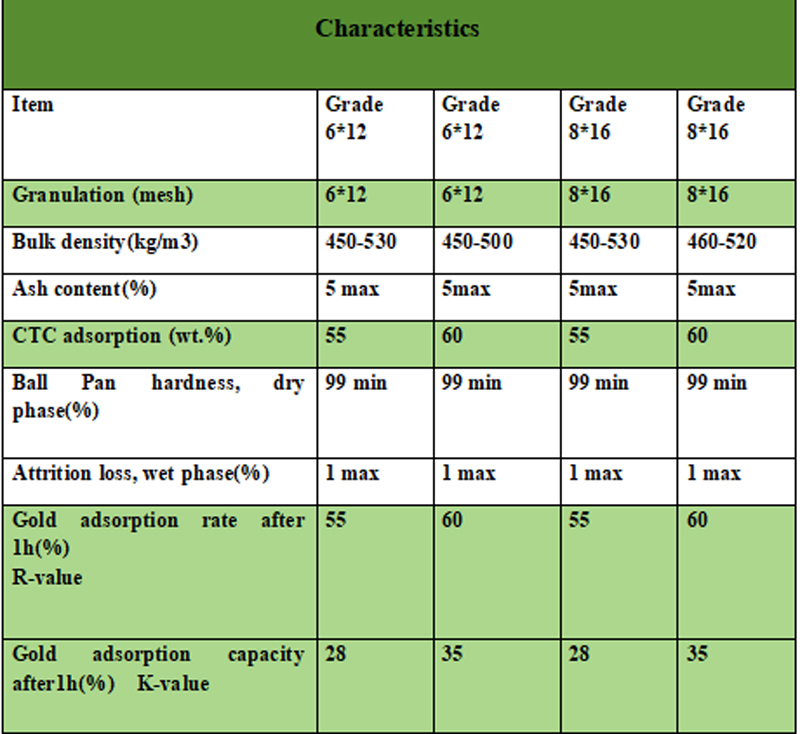
The carbon-in-pulp process (CIP) is a process in which activatedcarbon is added to the cyanide slurry to adsorb the dissolved gold on the activated carbon, and then the gold is extracted from the activated carbon. The main steps include preparation of leaching raw materials, stirring leaching and countercurrent carbon adsorption, desorption of gold-loaded carbon, electrolysis, smelting ingot making and carbon regeneration. CIP is suitable for amalgamated tailings, gravity separation tailings or muddy oxidized ores, with a recovery rate of up to 90%. The carbon-in-pulp process (CIP) has the advantages of high recovery rate and simple operation, and is particularly suitable for processing gold mines with high mud content. However, the process also has high investment and operating costs, operational complexity, and potential impacts on the environment and safety.
Carbon-in-place leaching (CIL)
Carbon-in-place leaching (CIL) combines the adsorption and extraction processes on the basis of carbon-in-place leaching. Activated carbon is added to the leaching tank, and leaching and adsorption are carried out simultaneously, that is, leaching and adsorption are carried out simultaneously, and then the gold-loaded carbon is desorbed and electrolyzed.
The advantages of carbon-in-place leaching (CIL) are that the number of leaching tanks is reduced, the process is shortened, and thus the infrastructure investment and production costs can be reduced; leaching and adsorption at the same time improve the dissolution kinetics of gold, which is conducive to the leaching and adsorption of gold. The pond leaching method is suitable for low-grade gold and silver mines and gold mines with less clay content, with a recovery rate between 50% and 70%. The design of the percolation tank is diverse, and the material can be wood, iron or cement. A false bottom and filter cloth are laid on the bottom to support the ore and promote the penetration of the leachate. The ore is placed in the leaching tank, and the circulating pump pumps the leachate prepared inthe lean liquid pool into the pool, and the precious liquid is subsequently replaced. Compared with the CIL and CIP methods, the pond leaching method has lower costs, can improve the economic benefits of low-grade gold mines, is easy to operate and has low labor costs. However, the initial construction investment of the pond leaching method is large, the leaching cycle is long, and the leaching efficiency is easily affected by factors such as the solvent dissolution rate, penetration rate and material properties.
Heap leaching is an economical and efficient gold extraction process, especially suitable for processing low-grade ores and tailings of 0.5-3g/t
Heap leaching is an economical and efficient gold extraction process, especially suitable for processing low-grade ores and tailings of 0.5-3g/t. The ore is crushed to an appropriate particle size and piled on a bottom pad. The ore pile is sprayed with sodium cyanide solution to dissolve gold and silver in the solution. Then, activated carbon adsorption, zinc replacement or electrolytic deposition are used to recover gold. Heap leaching has the advantages of simple process, low investment, quick effect and low cost. The gold recovery rate can reach 50-90%, so that the ore that originally had no economic value can be recycled. The tailings are discharged after disinfection, realizing the economic recovery and utilization of resources.
During the gold ore selection process, the ore dressing plant should first conduct a ore dressing test, analyze the ore properties in detail, and formulate an optimized ore dressing plan based on the actual situation of the gold ore dressing plant, investment and other factors, so as to achieve efficient selection of concentrates and improve theore dressing recovery rate, and achieve an ideal return on investment.